![]()
Detection Capabilities
- Detection height for free-standing and wall applications: 6.1 m (20 ft)
- Detection height for fence installations: 7.3 m (24 ft)
- Zone length: ~ 150 m (500 ft)
XField is a terrain-following volumetric sensor that generates an invisible field of energy around parallel sets of wires. When an intruder enters the field, an alarm is generated. XField is designed for high-security environments and can be used in free-standing, fence-mounted, roof and wall applications. In particular, XField has been a popular choice for nuclear power facilities due to its adjustable height capabilities.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) analyzes the capacitance of XField’s sense wires and uses the amplitude of change (size of the intruder), rate of change (movement of the intruder) and the time the target spends within the detection fields to qualify the alarm. Each XField processor provides two zones of detection, A and B. Each zone can be configured with either 4 wires (two field wire and two sense wires) or 5 wires (three field wires and two sensor wires). To increase the height of the detection area, the A and B zones can be stacked.
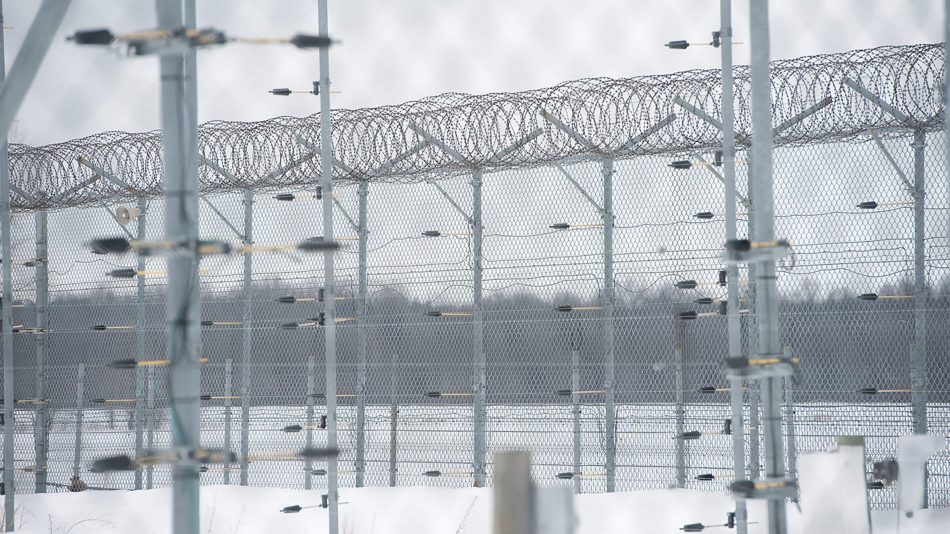

With heights of up to 7.3 m (24 ft) and widths as low as 0.5 m (1.6 ft), XField’s tall but narrow detection zone provides ultra-high security that remains unaffected by nearby activity.
The visible wires act as a deterrent for would-be intruders while the invisible vertical detection field generates an alarm on intrusion attempts.
XField is able to distinguish the difference between capacitive and resistive changes, resulting in an ultra-low nuisance alarm rate while maintaining a high Probability of detection (Pd) in all weather conditions.
XField’s mounting brackets and insulators are made of durable and corrosion-resistant materials designed to survive years of outdoor exposure.
With on-board relay outputs, auxiliary inputs, and support for RS-422 and fiber optic communication cards, XField can work with virtually any security system.
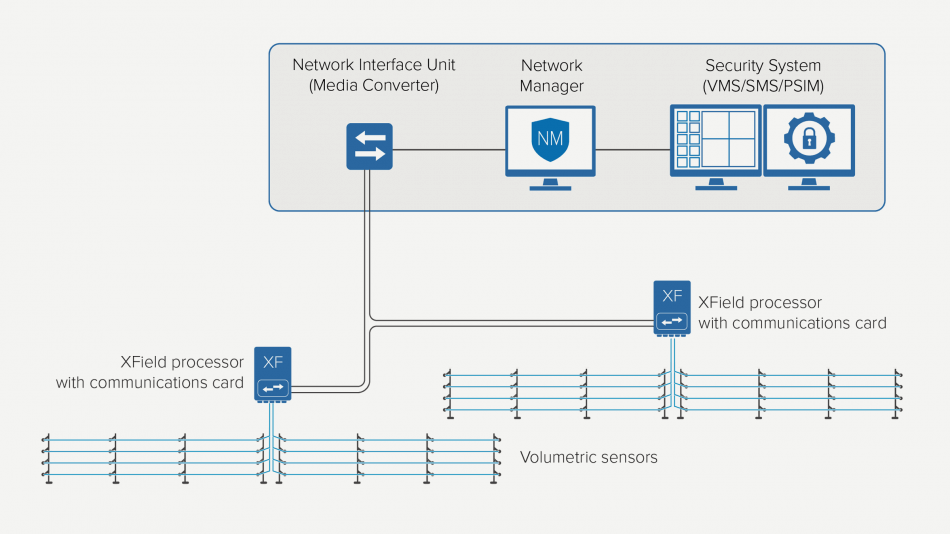
XField uses the same configuration and integration software as other Senstar products, reducing training requirements while increasing operational efficiencies. The device is configured and calibrated with easy-to-use Windows®-based software over a USB or network connection. Alarms, control, and status information is managed by the Network Manager software, which provides a common unified interface for Senstar’s video and security management software as well as other industry-leading third-party systems.
XField typically communicates with the security system via RS-422 or fiber optic interfaces. The communications network may be shared with other Senstar sensors to reduce infrastructure requirements. Integrations using output relays are also supported.
Return to Category
View All Documents
View General Info
A recent article posted on securitymagazine.com summarized six challenges associated with securing the perimeters of large facilities. In our last post, we looked at the first three challenges. In Part 2...
A recent article posted on securitymagazine.com summarized six challenges associated with securing the perimeters of large facilities. In Part 1 of this article, we examine the first three challenges in greater...
Maintaining a secure perimeter from both internal and external threats is a fundamental requirement for correctional facilities. The perimeter’s security infrastructure, as part of a comprehensive physical protection system (PPS), includes...