Alarm Zones VS Virtual Fences
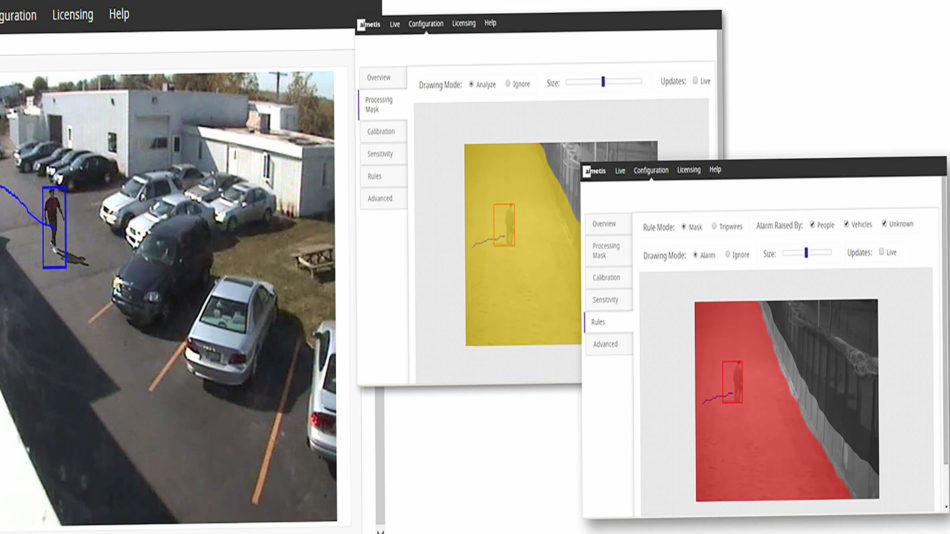
Video analytics are powerful and versatile. They enhance live video surveillance and streamline security operations before, during, and after an incident. Because of their power and flexibility, different approaches can often be used to accomplish the same goal. For example, Senstar outdoor tracking analytics, the edge-based Outdoor Object Tracker (OOT) and the server-based Outdoor People and Vehicle Tracking (OPVT), can use either area-masking (alarm zones) or tripwire (virtual fence) rules to monitor protected areas and trigger intrusion alarms.
- Alarm Zones – An alarm zone is a designated area drawn into a video surveillance scene using a mask rule. If motion is detected within the masked area, an alarm will be generated. The main benefit of alarm zones is their high accuracy when identifying objects moving within the designated field.
- Virtual Fences – A virtual fence can be used to enclose or wall-off a designated area. Tripwire lines are drawn to define area boundaries and determine which direction an object needs to travel in order to trigger an alarm. Virtual fences are excellent at determining the direction that an object is moving in and are useful for monitoring people and vehicles when entering or exiting an area, such as a gate or designated exit door.
Click here to download an article that discusses the differences between alarm zones and virtual fences and provides best-practice guidelines on how and when to use them in different applications.
